Beyond meeting global commitments and goals—including the Paris Agreement and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)—Green Finance (GreenFi) or Climate Finance, whether sustainable or regenerative, is vital for addressing the urgent environmental challenges we face today. Blockchain-based solutions and DeFi are emerging as key drivers of such financial tools and instruments, improving ease of funding, transparency in fund sources and usage, and allowing the global masses to be a part of what should be democratized – our survival.
Nine years ago, on 12th December, 196 parties entered into the Paris Agreement, the international treaty on climate change. The agreement has a lofty ambition – to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, with efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Current policies and pledges are projected to lead to a global temperature rise of about 2.7°C by the end of the century.
The world is far from achieving its goals.
The global economy is reliant on fossil fuels and non-renewable resources. The result? Increased greenhouse gas emissions—the primary drivers of climate change. The solution lies in transitioning to a low-carbon, sustainable economy. This requires capital mobilization towards activities that foster sustainability and minimize environmental harm.
In short, it boils down (pun intended) to finance.
The Urgent Need for Environmental-Focused Finance
Let’s look at some numbers.
7 million premature deaths are caused each year by air pollution, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
68% of vertebrate wildlife populations have been lost since 1970 due to habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change, per the World Wildlife Fund (WWF).
Climate change-related risks could result in $2.5 trillion in economic losses by 2030, estimated by the World Economic Forum (WEF).
Look up online, and you’ll find more alarming numbers highlighting the urgency with which we need to fund and implement measures to mitigate and reverse the drastic effects of climate change.
This is where environmentally-first finance comes into the picture. And blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi) are key to unlocking the potential of such mechanisms.
A Primer to Environmentally Conscious Finance
Our present-day mechanisms can be categorized into degenerative, sustainable, and regenerative systems.
Degenerative systems use more energy than they produce, making them unsustainable. Currently, we operate within a degenerative framework.
As a result, we’ve crossed six of the nine planetary boundaries, putting human and environmental health at serious risk.
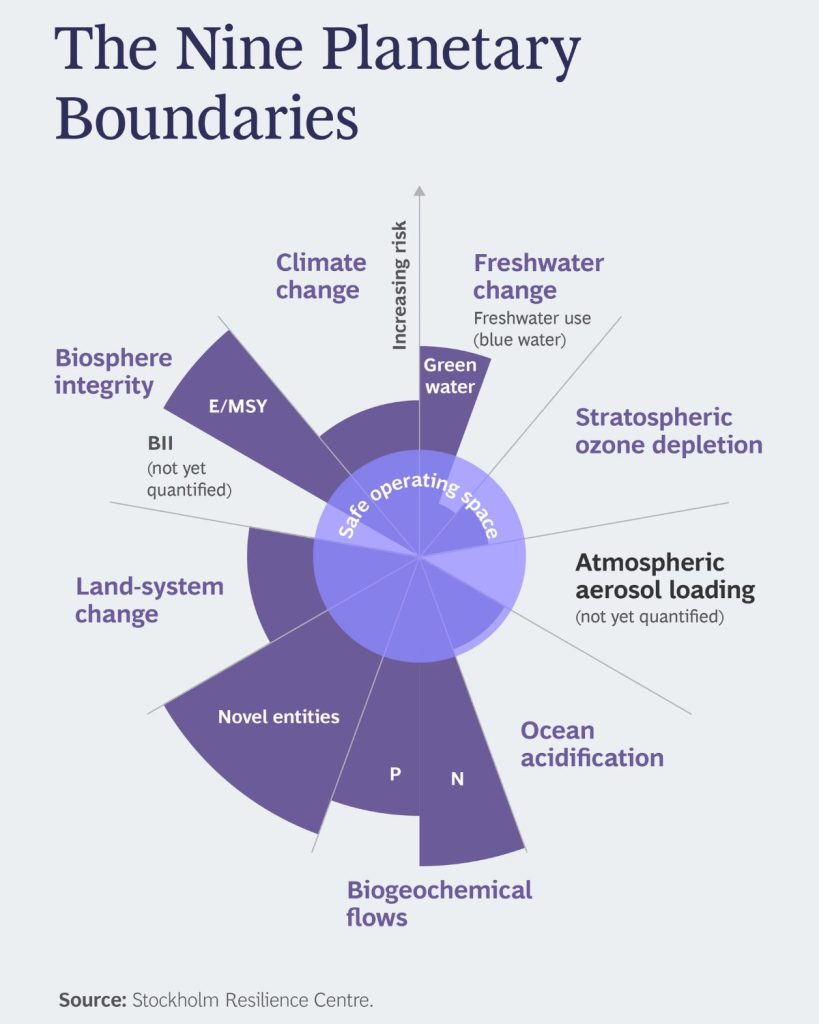
Sustainable systems use resources wisely, ensuring they are not depleted faster than they can be replenished. In a world dominated by degenerative systems, aiming for sustainability is an important goal.
However, our ultimate objective should be to move beyond sustainability, towards regeneration.
Regenerative systems focus on activities that not only sustain but actively enhance the environment. These activities help increase productivity, improve health, boost resilience, and extend the longevity of ecosystems. By giving back more than they take, regenerative systems create a positive cycle of renewal and growth.
A plethora of projects lie within sustainable and regenerative systems. The funding routes, tools, and mechanisms for these projects are termed green/climate finance, sustainable finance, and regenerative finance, depending on the scope, and whether the undertaking is mitigatory or restorative in nature.
Sustainable Finance, Green Finance (GreenFi), and Regenerative Finance (ReFi) support the transition to a low-carbon, sustainable economy while addressing global challenges such as climate change and environmental risks.
What is Sustainable Finance?
Sustainable finance involves making investment and financial decisions, taking into account environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, to foster sustainable economic growth.
The goal is to create long-term value by channeling financial resources into projects and initiatives that promote sustainability, reduce environmental impacts, and address social issues.
What is ReFi?
Regenerative finance (ReFi) goes a step beyond sustainable finance. Its investments are focused on reversing the negative impacts of traditional capitalism, and replenishing environmental and societal resources, rather than merely reducing its negative side effects.
ReFi aims to address systemic problems like climate change, by supporting a shift from an extractive economy—traditional finance that places short-term profits ahead of long-term sustainability—to a regenerative one.

By aligning the right incentives, ReFi creates economic systems that generate returns while regenerating the natural world.
What is Climate Finance or Green Finance?
Green finance, also known as climate finance, funds projects that benefit the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting renewable energy. Its goal is to tackle climate change and facilitate a shift to a low-carbon economy.
GreenFi projects include:
- Renewable energy and energy efficiency projects
- Pollution prevention and control measures
- Biodiversity conservation efforts
- Circular economy initiatives
- Sustainable use of natural resources and land management
Current Market for Climate Finance
Between 2011 and 2022, $4.8 trillion was committed to the finance initiatives, averaging $480 billion annually. Today’s investment levels have risen to around $630 billion annually, but this is still far below the $3 trillion needed each year, projected to reach $6 trillion by 2050, to limit global temperature rise to 1.5°C.
Given the strain on public budgets and tight borrowing conditions, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) emphasizes the crucial role of private finance. Private markets are stepping up, with recent commitments from four major banks totaling $5.5 trillion by 2030 – J.P. Morgan, Barclays, HSBC, and Citigroup. Additionally, 450 financial institutions have joined the Glasgow Financial Alliance for Net Zero to achieve net-zero emissions. Private companies, including Sony, DHL, Lufthansa, Cemex, and Delta Airlines, are also committing to emissions reductions through voluntary carbon markets.
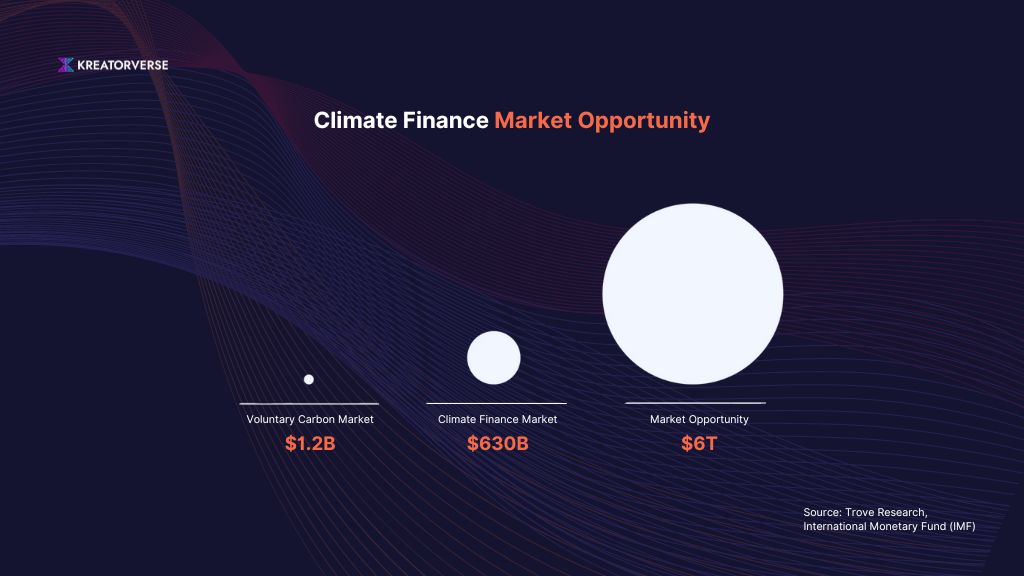
In 2022, the voluntary carbon market grew by 20% to $1.2 billion, and the number of companies setting net-zero targets more than doubled. McKinsey & Company estimates that global demand for carbon credits could increase 15-fold by 2030 and 100-fold by 2050.
Climate Finance is plagued with Challenges
Climate or GreenFi tools, whether mitigative or restorative, have been around for a while now. With ambitious goals to be achieved in a short time window, the pressure is on for these projects to deliver. But as with everything else, GreenFi has its own set of challenges.
From the lack of globally accepted standards and high barriers to entry to technology obstacles and aligning with traditional finance, GreenFi and ReFi projects have mountains to overcome.

Addressing these challenges requires coordinated efforts from policymakers, financial institutions, investors, and other stakeholders.
However, most of these challenges can be overcome with the right kind of technology – one that’s transparent, immutable, accessible to all, and scalable.
How Blockchain and DeFi can empower Environmental-Focused Finance mechanisms
Blockchain’s core capabilities, like transparency, immutability, decentralization, and trustless automation, have immense potential to drive innovation that helps address the climate crisis. Blockchain-based decentralized finance (DeFi) can realign incentives, reshape capital flows, and enable coordination at an unprecedented global scale.
- Lack of standardization and definitions: No standard definition for sustainable, green, and regenerative finance exists. This makes it difficult for investors to compare and trust the sustainability credentials of different projects.
Solution: Blockchain provides standardized protocols and transparent records, creating a universal framework for defining and tracking sustainability metrics.
- Greenwashing: Some companies may exaggerate or misrepresent their environmental efforts to appear more sustainable than they are. Known as greenwashing, this undermines investor confidence, diverting funds from genuinely impactful projects.
Solution: Blockchain’s immutable ledger ensures transparency and traceability, making it difficult for companies to misrepresent their sustainability efforts. Veridium leverages blockchain to create transparent carbon credit markets, reducing the risk of greenwashing by providing verifiable records of carbon offsets.
- Data availability and quality: Reliable and consistent data on the ESG performance of projects and companies is often lacking. Without high-quality data, it’s challenging to assess the true impact of investments.
Solution: Decentralization provides a transparent way to collect, store, and share high-quality ESG data, improving data reliability. IBM Food Trust uses blockchain to track food supply chains, providing detailed data on sustainability practices and improving data quality.
- High initial costs: Sustainable and regenerative projects often require significant upfront investment, which can be a barrier for some investors. The perceived financial risk associated with these projects can also deter investment.
Solution: DeFi platforms lower the barriers to entry by offering decentralized loans and crowdfunding options, reducing the need for large upfront investments. SolarCoin incentivizes solar energy production by rewarding solar energy producers with cryptocurrency, helping to offset initial investment costs.
- Regulatory and policy uncertainty: Clear, supportive, and stable policy frameworks are necessary to encourage investment in sustainable projects, which are currently lacking.
Solution: Smart contracts on blockchain automate compliance with regulations, reducing uncertainty and ensuring adherence to regional policies. The Energy Web Foundation (EWF) uses blockchain to create regulatory-compliant solutions for renewable energy markets, ensuring that projects meet local regulations.
- Short-termism: Many financial markets and investors focus on short-term returns rather than long-term sustainability. This discourages investments in projects with significant long-term benefits but requires longer time horizons to become profitable.
Solution: Blockchain and DeFi platforms facilitate long-term investment structures, such as tokenized assets and smart contracts that lock in funds for extended periods. ImpactDAO is a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) that funds long-term sustainability projects through tokenized investments and community governance.
“Climate change is the result of the greatest market failure that the world has seen.”
Knut N. Kjær, Executive Chairman, Sector Asset Management and first manager of the Government Pension Fund of Norway, on the need to consider the long term when accounting for the risks and returns of their investments
- Market liquidity: Some sustainable and regenerative assets, such as green bonds or carbon credits, may suffer from lower liquidity compared to traditional financial assets. This can make it harder for investors to enter and exit positions.
Solution: Tokenization of assets on the blockchain can be leveraged to enable fractional ownership and easy transfer of assets, making projects accessible to investors. Swarm Markets provides a platform for tokenizing real-world assets, including green bonds, improving liquidity and accessibility for investors.
- Technological barriers: Technical complexities, scalability issues, and lack of widespread understanding can hinder their effective implementation in sustainable finance.
Solution: Open-source blockchain projects and DeFi platforms promote widespread understanding and adoption by providing accessible technology and educational resources. Ethereum’s open-source blockchain platform supports numerous DeFi projects focused on sustainability, offering tools and resources for developers and users.
- Impact measurement and reporting: Measuring the actual impact of sustainable investments can be complex and resource-intensive. There is a need for robust frameworks and methodologies to assess and report on the environmental and social outcomes of investments accurately.
Solution: Blockchain ensures transparent and accurate impact reporting by recording all transactions and outcomes on an immutable ledger. Poseidon Foundation uses blockchain to track and verify the impact of its carbon credit purchases, providing transparent and reliable impact reports.
- Access to capital: Smaller projects, particularly in developing countries, struggle to access the necessary capital. This can be due to a lack of financial infrastructure, higher perceived risks, or limited investor awareness.
Solution: DeFi platforms enable direct access to global capital, bypassing traditional financial intermediaries and lowering the cost of capital for small projects. Moeda Seeds uses blockchain to provide microloans to small businesses and sustainable projects in developing countries, improving access to capital.
- Evolving investor expectations: Investors increasingly demand that their investments deliver not only financial returns but also measurable positive impacts. Financial institutions and project developers must adapt to these expectations, which can be challenging without clear guidelines and metrics.
Solution: Blockchain can provide verifiable ESG data and impact metrics, aligning with investor demands for transparency and measurable outcomes. Evercity leverages blockchain to provide end-to-end solutions for impact measurement and reporting, meeting the evolving expectations of sustainable investors.
- Integration with traditional finance: Integrating sustainable finance practices into traditional financial systems can be challenging – aligning risk assessment models, investment strategies, and performance metrics with sustainability goals.
Solution: Blockchain can integrate with traditional financial systems through APIs and interoperable platforms, facilitating the adoption of sustainable practices. ConsenSys Codefi provides blockchain-based solutions that integrate with existing financial infrastructure, enabling seamless adoption of sustainable finance practices.
Green Financing Tools with Blockchain and DeFi Solutions
Climate financing tools, enhanced by blockchain and DeFi solutions, collectively help channel investment towards sustainable and climate-resilient development, supporting the global transition to a low-carbon economy.
Green Tokenization
Renewable energy projects, sustainable farms, or carbon offset initiatives can be tokenized as tradable assets on DeFi platforms. This allows for fractional ownership, making green investments more accessible to a wider range of investors.
By tokenizing green assets, we can democratize investments in sustainability, opening the doors for small investors to contribute to and benefit from environmentally friendly projects.
Peer-to-Peer Green Lending
DeFi platforms can connect individual investors directly with green projects, eliminating the need for traditional financial intermediaries and potentially lowering transaction costs. This peer-to-peer model ensures that more funds go directly to the projects themselves, increasing their impact and efficiency. Investors can see exactly where their money is going and the benefits it’s creating, fostering a stronger connection to their investments.
Impact DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations)
Communities with a shared interest in green initiatives can pool resources and make collective investment decisions through DAOs. This fosters transparency and democratic participation in green finance. Impact DAOs empower individuals to have a say in where their money goes, ensuring that investments align with the community’s values and goals. This model not only promotes financial inclusion but also enhances accountability and trust within the ecosystem.
Blockchain and DeFi-powered Climate Finance and ReFi projects in action
Toucan
In the carbon removal space, Toucan builds infrastructure to enhance the carbon removal market through blockchain-based trading for improved transparency and accessibility. Their platform allows individuals and organizations to participate in carbon markets, promoting demand for climate solutions.

Their key product, CHAR, facilitates the tokenization of carbon credits, allowing them to be traded on the blockchain. Collaborating with partners like Neutral and Celo, and sourcing initial credits from Exomad and American BioCarbon, Toucan has successfully bridged millions of carbon offsets to the blockchain.
KlimaDAO
KlimaDAO is a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) that leverages decentralized finance (DeFi) to invest in carbon dioxide removal projects, aiming to combat climate change.
KlimaDAO’s KLIMA token incentivizes participation in carbon markets, using blockchain technology and tokenomics to encourage the purchase, staking, and retirement of carbon credits.
By pooling resources from a community of like-minded individuals, KlimaDAO demonstrates the power of collective action in reducing atmospheric carbon levels. The autonomous protocol operates as a market maker for environmental commodities, with its evolution guided by the DAO community.
Regen Network
Regen Network leverages blockchain technology to support regenerative agriculture by connecting farmers with eco-conscious consumers and providing financial incentives for sustainable practices.
The platform facilitates transparent ecological accounting and enables stakeholders to value natural assets like forests, streams, and grasslands.

ReFiDAO
ReFiDAO is a decentralized network aimed at addressing climate change, biodiversity loss, and social injustice by promoting regenerative finance. It uses blockchain and Web3 technology to create a global movement of local startup communities focused on regenerating the Earth.
ReFiDAO facilitates the development of local communities, organizes events, and supports various projects that drive ecological and social regeneration. By leveraging a knowledge graph and a network of online guilds and working groups, ReFiDAO coordinates efforts to create a just and sustainable economic system.
Flowcarbon
Flowcarbon focuses on scaling carbon removal projects through innovative structured finance, by merging investment banking, project development, and carbon credit sales expertise.
The company enables the development and financing of projects including biochar, enhanced rock weathering, direct air capture, and renewable natural gas. The company also provides corporate portfolio services that incorporate highly durable carbon credits from project developers around the globe.
Flowcarbon has been recognized as one of America’s Top GreenTech Companies in 2024 by TIME and Statista for its innovative approach to scaling the voluntary carbon market through both traditional and blockchain-based project financing products.
Others
Other notable GreenFi and ReFi projects that are blockchain- and DeFi-based include
- Ivy Protocol: Involved in early financing of climate protection projects through corresponding tokens. The platform aims to accelerate the funding and implementation of carbon offset projects, making it easier for developers to secure necessary resources.
- Solid World DAO: Leverages DeFi to fund and support climate protection initiatives. It provides liquidity and financial tools to developers of carbon offset projects, ensuring that these initiatives receive the funding they need to succeed.
- Open Forest Protocol: Uses blockchain to collect and manage digital climate data. This platform facilitates the transparent and efficient recording of environmental data, which can be used to monitor and verify carbon offset projects.
- Climate Action Data Trust: Decentralized metadata platform designed to provide reliable and accessible climate data. It helps various stakeholders, including NGOs and government bodies, to access and utilize climate-related data for informed decision-making.
- MOSS: Specializes in tokenizing carbon credits from Amazon rainforest conservation and reforestation projects. By creating digital tokens representing carbon credits, MOSS enables the trading of these credits on blockchain platforms, promoting transparency and accessibility.
- Tupan: A notable project in the ReFi space that prioritizes the protection of the Amazon rainforest. It aims to leverage blockchain technology to create financial incentives for conservation efforts.
- The AEternals: Focuses on preserving the Amazon rainforest through innovative funding mechanisms. It uses blockchain to ensure transparency and traceability in its conservation efforts.
- Nemus: Acquires at-risk land in the Amazon rainforest and issues collectible NFTs tied to specific geolocations within this land. The proceeds from these NFT sales fund conservation and reforestation efforts, creating a direct link between digital assets and real-world environmental impact.
Have a Climate Finance idea?
Leverage blockchain technology to build, scale and launch your project, no matter the stage or size.
The Road Ahead in Harnessing Blockchain and DeFi for Climate Finance and ReFi
The International Energy Agency (IEA) reported that renewable energy investments reached $303.5 billion in 2020, but this figure needs to triple by 2030 to meet climate objectives.
The World Bank estimates that achieving a low-carbon transition by 2030 could require up to $90 trillion in investments in sustainable solutions.
It’s clear – financial backing from finance and ReFi is essential to transition these solutions from pilot projects to broader implementation.
“We have the solutions and there is no shortage of capital that needs to be invested in the new low-carbon economy. We need to design the future sustainable world in which to invest that capital.”
Sean Kidney, CEO, Climate Bonds
The digital revolution impacts industries without discrimination, and financial institutions should capitalize on this revolution with blockchain technologies. Despite the hype and the skepticism, asset tokenization is paving the way for Web3 maturity and acceptance. With this comes wealth democratization, and financial inclusion.
As global policies increasingly support sustainable practices, investments in green and regenerative projects are becoming more appealing and less risky. The CDP (formerly Carbon Disclosure Project) indicates that companies with strong ESG performance often outperform their peers financially, highlighting the economic advantages of sustainable investments.
The integration of GreenFi and DeFi marks a significant advancement toward a sustainable future. Utilizing the transparency, efficiency, and inclusivity of blockchain technologies can expedite the shift to a green economy. As these innovations progress, we stand at the cusp of exciting opportunities for investors, communities, and the planet.
Hopefully, these projects will take us to where we ought to be, and save us from a grim future.

